Vitiligo is a skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by the loss of pigmentation, resulting in white patches on the skin. While the condition is not life-threatening, it can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. In this article, we will discuss the signs and symptoms of vitiligo, how it develops, risk factors, and triggers, diagnosing vitiligo, treatment options, ongoing studies, and potential therapies.
Symptoms and Signs of Vitiligo
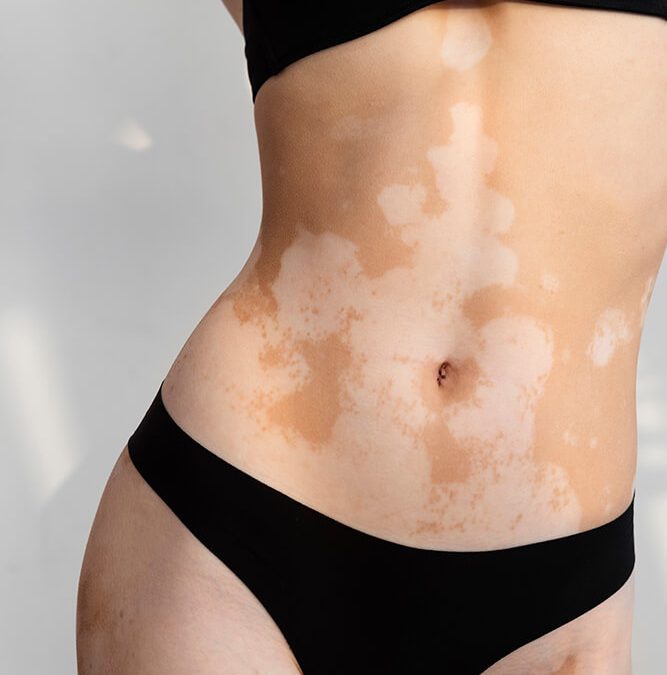
Vitiligo is most commonly found on the face, hands, and feet, but it can also appear on other areas of the body. The loss of pigmentation can happen quickly or gradually, and the severity can vary from person to person.
Common Symptoms
- Loss of skin colour in patches
- Premature whitening of hair
- Loss of colour in the mucous membranes, such as the mouth and nose
- Sunburn easily on affected skin
Early Signs and Symptoms
- Lightened or white areas of skin
- Premature greying of the hair on the scalp, eyelashes, eyebrows, or beard

How Vitiligo Develops
The development of vitiligo can occur in different stages, and it can progress at different rates for each person.
Stages
- Focal: Depigmentation is limited to one or a few areas.
- Segmental: Depigmentation occurs on one side of the body and is generally limited to certain areas.
- Generalized: Depigmentation occurs on different parts of the body, often symmetrically.
Progression
The loss of pigmentation may stop on its own, but it can also continue to progress over time. The extent and rate of progression are unpredictable.
Risk Factors and Triggers
Although the exact cause of vitiligo is unknown, there are some risk factors and triggers that have been identified.
Genetics
There is a genetic predisposition for vitiligo, and it is more common in people with a family history of the condition.
Environmental Factors
There is also evidence that environmental factors can trigger vitiligo, including:
- Sunburn or skin injury
- Exposure to chemicals
- Emotional stress
Diagnosing Vitiligo
A dermatologist can diagnose vitiligo based on a medical history and physical examination.

Medical History and Physical Examination
The dermatologist will review the patient’s medical history, ask about any symptoms, and perform a physical examination to look for signs of vitiligo.
Diagnostic Tests
In some cases, the dermatologist may order diagnostic tests, such as a skin biopsy or blood test, to rule out other skin conditions.
Treatment Options for Vitiligo
Although there is no cure for vitiligo, there are treatments that can help to improve the appearance of the skin.
Medications
Topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and vitamin D analogues are medications that can help to repigment the skin.
Light Therapy
Light therapy, also known as phototherapy, involves the use of UV light to stimulate the production of melanin in the skin.
Research and Future Prospects
There are ongoing studies into the causes and treatments of vitiligo.
Ongoing Studies
Researchers are investigating the use of stem cells to repigment the skin, as well as the role of the immune system in the development of vitiligo.
Potential Therapies
New therapies, such as Janus kinase inhibitors and gene therapy, are showing promise in clinical trials.
Conclusion
In conclusion, vitiligo and its signs and symptoms are a common skin condition that can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. While there is no cure, there are treatments available to help manage the symptoms. If you suspect that you may have vitiligo, it is important to consult with a dermatologist to receive an accurate diagnosis and discuss treatment options.
At Colourderma, we specialize in providing skin care and camouflage solutions for people with vitiligo. Our expert team of professionals can work with you to create a personalized plan that meets your individual needs and helps you feel confident in your own skin.

FAQs about the Signs and Symptoms of Vitiligo
- Is vitiligo contagious?
No, vitiligo is not contagious and cannot be spread from person to person.
- Can vitiligo be prevented?
There is currently no known way to prevent vitiligo, but avoiding triggers such as sunburn and skin injury may help to reduce the risk.
- Can vitiligo be cured?
There is no cure for vitiligo, but treatments can help to manage the symptoms and improve the appearance of the skin.
- Can makeup be used to cover vitiligo patches?
Yes, makeup can be used to cover vitiligo patches. At Colourderma, we offer specialized makeup products and techniques to help camouflage the skin and improve the appearance of vitiligo patches.
- Is there ongoing research into vitiligo?
Yes, there is ongoing research into the causes and treatments of vitiligo. Researchers are investigating new therapies, such as stem cell treatments and gene therapy, that may offer hope for people with vitiligo in the future.

Recent Comments